Comparing Architectural Styles: Portuguese Traditional vs. Modern Design
Exploring the Richness of Portuguese Traditional Architecture
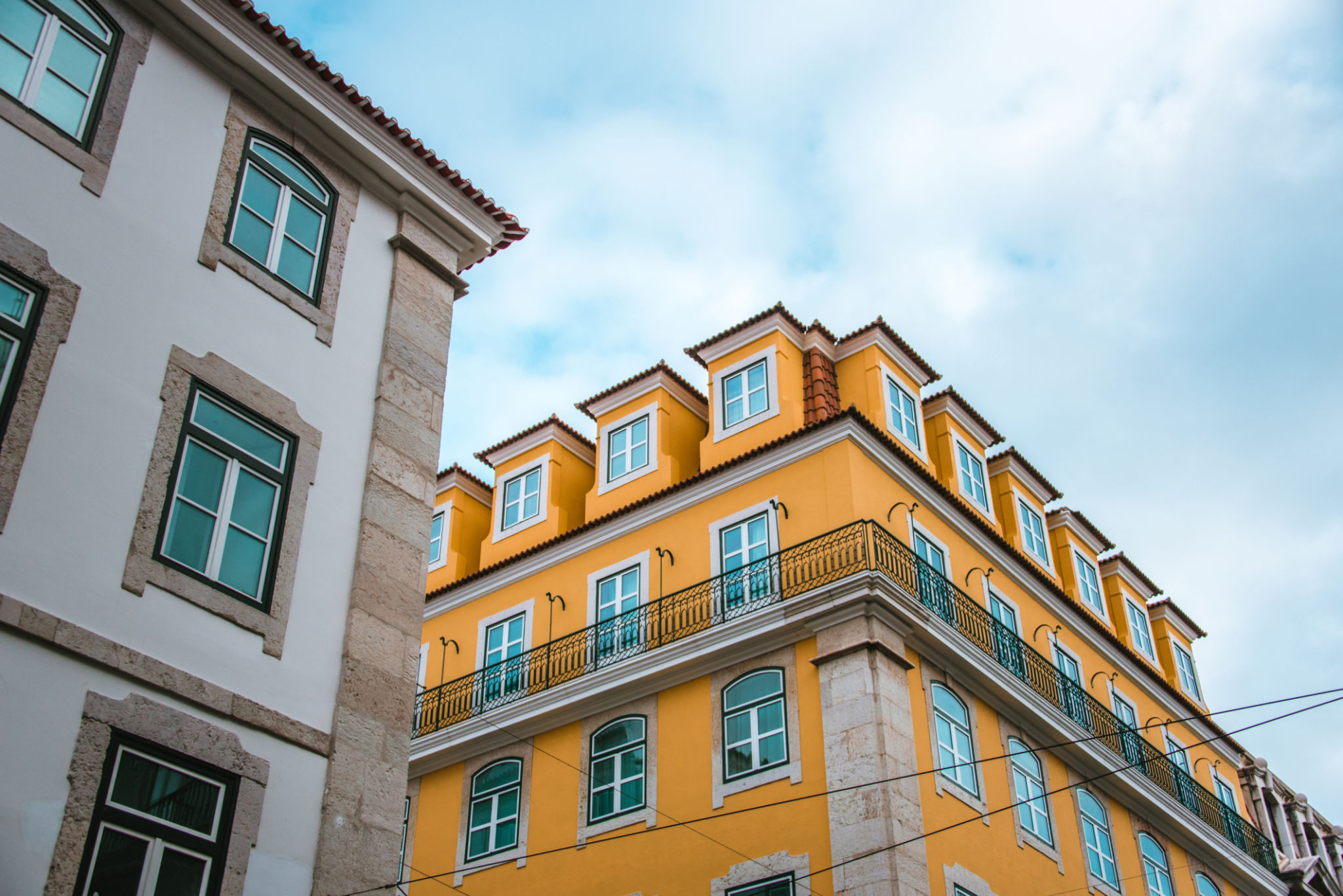
Portuguese traditional architecture is a captivating blend of historical influences and local cultural elements. This style is characterized by its intricate tile work, also known as azulejos, and the use of natural materials such as stone and wood. The architectural style reflects Portugal's maritime history and its connections with various cultures across the globe.
In traditional Portuguese buildings, you'll often find Manueline and Gothic influences, which are evident in the ornate carvings and detailed embellishments. These features contribute to the charm and elegance of structures like monasteries, churches, and palaces. The warm color palette, typically featuring whites, blues, and yellows, adds a distinct touch to the facades of these timeless structures.

The Essence of Modern Design
Modern design, in contrast, embraces simplicity and functionality. It often incorporates clean lines, open spaces, and minimalistic elements. The use of innovative materials such as steel, glass, and concrete is prevalent, offering a stark contrast to the ornate details of traditional architecture.
A key feature of modern architecture is its focus on sustainability and energy efficiency. Architects strive to create structures that not only look aesthetically pleasing but also have a minimal environmental impact. This approach often results in buildings that are both forward-thinking and respectful of their surroundings.
Comparative Elements: Aesthetic Appeal
When comparing the aesthetic appeal of Portuguese traditional versus modern design, the differences are striking yet complementary. Traditional architecture appeals to those who appreciate history and craftsmanship, with each building telling a story through its intricate details. On the other hand, modern design attracts individuals who prefer a more streamlined and contemporary look.
The juxtaposition of these styles can often be seen in urban landscapes where modern skyscrapers stand alongside historic buildings. This combination creates a dynamic visual dialogue between the past and the present.

Functional Differences
The functional aspects of these architectural styles also differ significantly. Traditional Portuguese buildings, with their thick walls and small windows, were designed to withstand the local climate, providing insulation against both cold winters and hot summers. These structures often feature courtyards or patios that offer shaded outdoor spaces for relaxation.
Modern architecture focuses on maximizing space and light. Large windows and open floor plans are common, allowing for natural light to permeate the interior spaces. This approach not only enhances comfort but also fosters a connection between indoor and outdoor environments.
Cultural Significance
Each style carries its own cultural significance. Traditional Portuguese architecture serves as a testament to the country's rich history and cultural heritage. It holds stories of past generations and reflects the diverse influences that have shaped Portugal over centuries.
Conversely, modern design represents progress and innovation. It speaks to contemporary values and future aspirations, often symbolizing technological advancement and a commitment to sustainable living.

Conclusion: Embracing Diversity in Architecture
The comparison between Portuguese traditional and modern design highlights the diversity and richness of architectural styles. Each style offers unique benefits, making them valuable in their own right. As cities evolve, embracing a blend of both traditional and modern elements can lead to urban landscapes that are vibrant, reflective, and inclusive.
Ultimately, whether you prefer the historical allure of traditional architecture or the sleek sophistication of modern design, both styles play an essential role in shaping our built environment.
